Identifying the right location to establish a business is a fundamental part of the basic strategy of any company in every industry. Selecting the exact right area and location is crucial not only for profitability, but also to help determine whether or not the business will be successful.
Iterative analysis of transaction, facility and asset data, along with geographic data, can provide valuable information that help all kind of retail businesses to choose the right location when establishing a site location. Without the right tools to manage large volumes of information and the help of GIS (geographic information system) a “traditional” data collection and analysis process would require a lot of time and money.
There are different optimization and suitability models for mobility-tested areas. The transformative potential of this type of analysis in the investment and selection of new locations is great, as it allows predicting the impact of important decision factors that may change over time and algorithmically optimizing location decisions.
Also read: “Geospatial data applied to the retail sector.”
PROBLEM
A U.S. hardware store chain, with hundreds of outlets in operation nationwide, needed, as part of its expansion strategy, to analyze new cities to determine their market potential and evaluate the opening of new outlets in those cities.
a
The process of data monetization, a concept that until recently was present only in conversations between technology experts, is now one of the recurring topics in strategic meetings at the management level in companies.
What is Data Monetization?
The concept of data monetization refers to the process of extracting, cleaning and analyzing the millions of data generated within a company, with the purpose of obtaining a benefit or economic value. This value can range from using the information to create performance indicators of the company’s own business and use them to optimize processes and make better strategic decisions, use it as input in the creation of other products or services, market it to third parties, share it with business partners, among others.
Why is it so relevant for companies?
Thanks to the accelerated advance of technology and the development of data science, there are more and more tools and methodologies available to obtain data from company information systems, such as servers, transactional platforms, operating systems, software programs, among others. Now any company can extract its own data from its systems, clean them, validate them, analyze them and extract value from them.
You may be interested in: “Business Strategy: How Geomarketing helps businesses.”
Codemotion.com reports that “… research shows that Big Data is responsible for generating about US$190 billion in revenue for companies, and this figure is expected to reach US$274 billion by 2022. Companies that adopt Big Data practices can increase their sales by up to 4%.”
What benefits does data monetization generate for companies?
From data-driven business models to creating tools to extract only certain types of information at a specific time in a production line, the uses of data monetization techniques are manifold.
- Optimization of data use
- Improved decision making and strategic planning processes
- Increased operational efficiency
- Improved customer understanding and buying experience
- Reduced operational costs
- Improved risk identification and prevention models
- Identification and exploitation of new business opportunities.
METHODOLOGY: EVALUATION OF AREAS WITH BIG DATA TECHNIQUES
In order to identify whether or not the cities have the potential to open new points of sale, and to determine within the cities the best locations to open new branches, PREDIK Data-Driven developed a methodology that collects geographic information, location and mobility data, pedestrian traffic with sociodemographic and subjective data on preferences and interests of the client potential customers.
First, it is necessary to define the profile of the client potential customer, which is done by taking into account the geographic location of the hardware store client online customer portfolio.

Then, the economic characteristics of potential customers are correlated, considering several variables of interest, including income level, consumer preferences and behavior patterns in social networks.
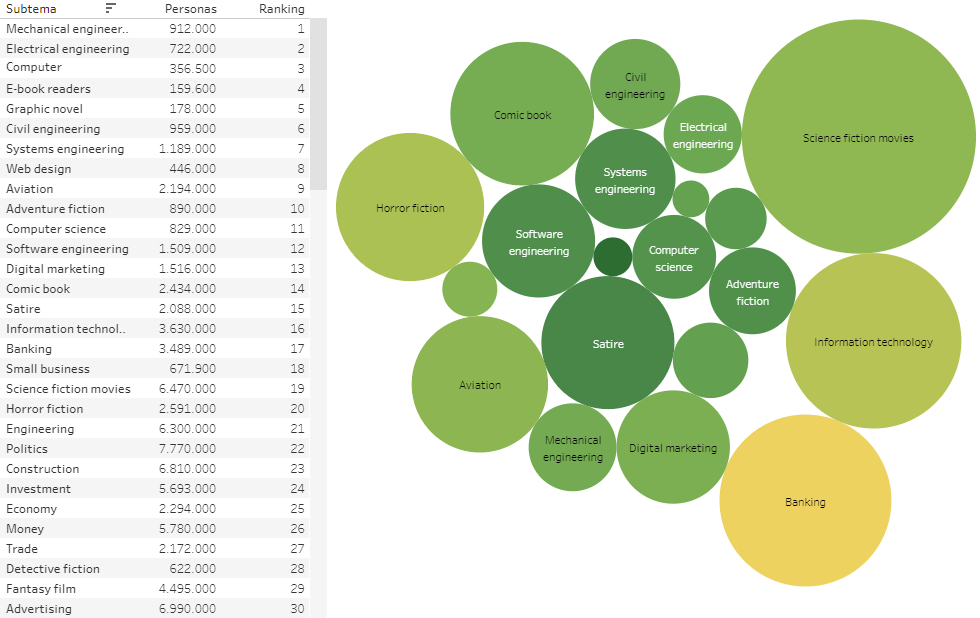
Subsequently, the characteristics of potential locations in the cities under evaluation are identified, and for this all relevant information is collected, both from locations where the client already has stores and locations of interest, such as:
- The population and its characteristics (income, spending composition).
- Economic and market evolution of the hardware store business in the cities of interest.
- Consumer preferences in social networks.
- Brand awareness in social media.
- Clustering and geographic segmentation, analyzing parcels and type of use (commercial, residential, etc).
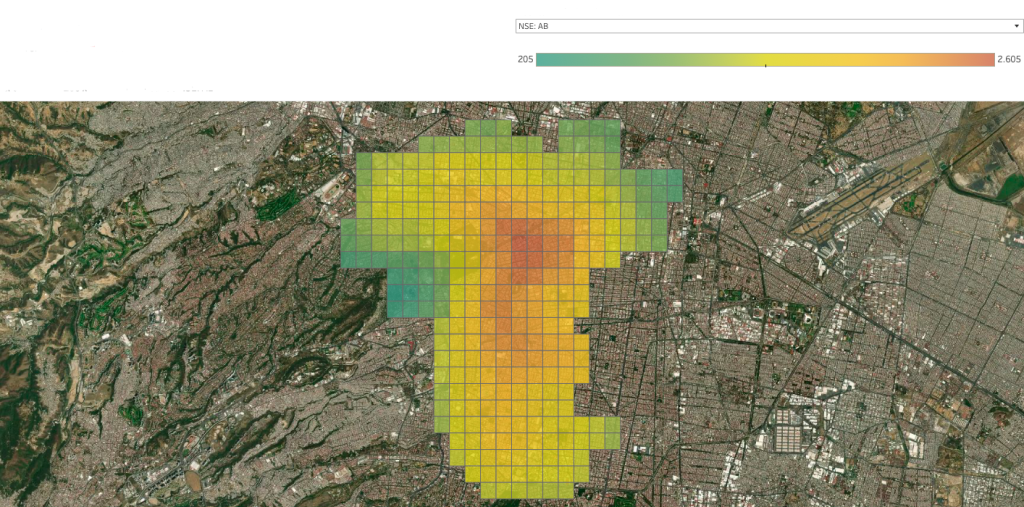
Based on the customer profile, the number of potential customers is estimated using a methodology that is based on the company’s own turnover figures, in this case, the hardware store chain. The customer shares the sales figures for each store, as well as the average ticket sales. This information is essential for estimating the potential sales of new outlets.
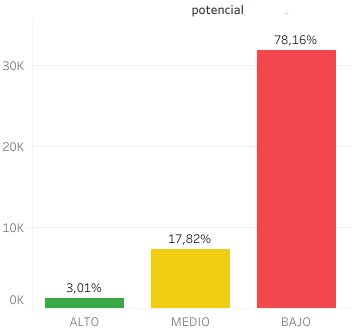
Subsequently, the commercial potential of the cities of interest is evaluated. By analyzing the characteristics of each potential location, the results of the analysis are compared with the characteristics of the cities where the client already has its points of sale. This comparative analysis is also done considering the performance of each store, market saturation and the number of total potential customers detected.
You may be interested in: “Industrial Localization and Big Data.”
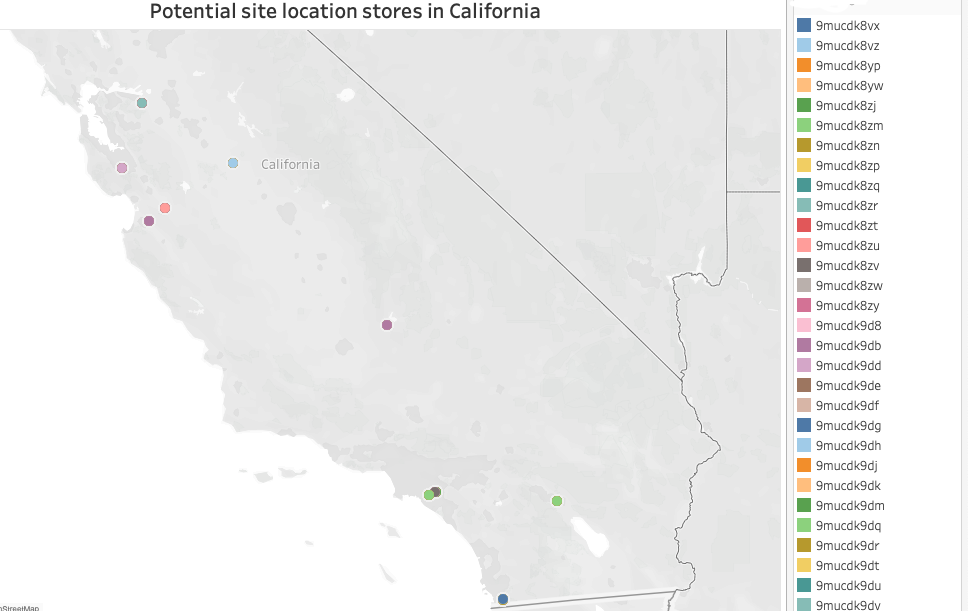
The final product is a list of locations of interest ranked by their business potential, including a sales estimate for each potential new store.
Contact us for more information about our solutions with Geospatial data for the retail sector


