Location Intelligence (LI) is a powerful tool that enables data-driven decisions. LI combines GIS, a wide range of geospatial data, artificial intelligence and BI. This is how it allows companies to understand their customers’ locations and interactions.
Imagine understanding your customers’ locations and behaviors, identifying new market opportunities, and optimizing your supply chain operations.
From retailers to insurance companies, finance companies to real estate companies, LI is used by many industries. Why? Because it helps improve efficiency, increase sales, and enhance customer experience.
We will explore the world of LI, understanding how it works. Its role in different industries, and the many benefits it can bring to businesses.
- Is Location Intelligence different than Business Intelligence?
- The importance of Location Intelligence for businesses?
- How are businesses using LI? (Applications location intelligence)
- How does Location Intelligence work?
- The role of Location Data in LI
- The role of Geospatial Data in LI
- The challenges of Location Intelligence
- How to develop the correct Location Intelligence Strategy?
Is Location Intelligence different than Business Intelligence?
The short answer is yes: LI differs from business intelligence (BI). LI specifically focused on geographic data and its applications. In contrast, BI focuses on analyzing data to make business decisions.
Location intelligence platforms add a layer of geographic data and analysis, allowing businesses to make location-based decisions.
” Location intelligence (LI) is a business intelligence (BI) tool capability that relates geographic contexts to business data.” Techtarget
The importance of Location Intelligence for businesses?
Location Intelligence has several business benefits, including increased efficiency, improved decision-making, and competitive advantage. LI can also improve the customer experience through personalized recommendations and offers based on a customer’s location.
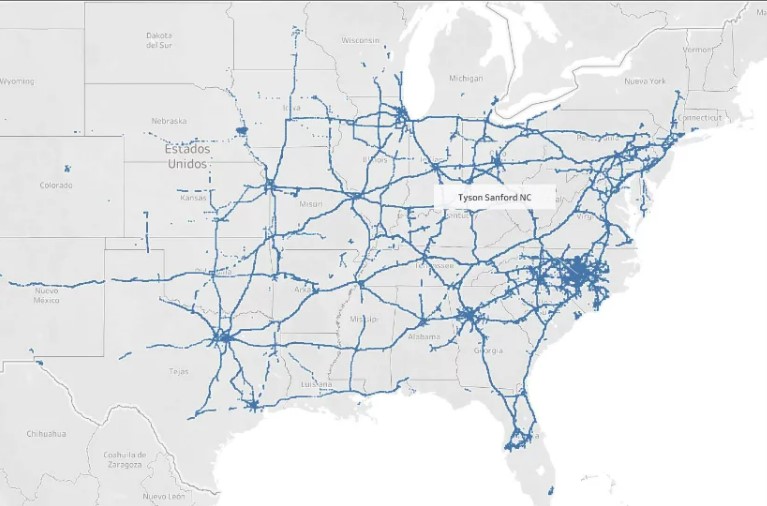
Customer understanding. LI allows businesses to understand their customers and their behavior better. These insights lead to increased sales and improved customer satisfaction.
You may also like to read: Customer Segmentation: How to Do With Predictive Location Intelligence
Improved Supply Chain operations. LI can also improve supply chain operations, identify new market opportunities, and make better decisions about site selection.
Increased Efficiency. Location intelligence can also help businesses become more efficient by identifying operation bottlenecks and delays. This efficiency boost can lead to cost savings and improved efficiency.
You may also like to read: Benefits of route planning with location intelligence
Competitive Advantage. Businesses can gain a competitive advantage by identifying new market opportunities, optimizing operations, and providing a better customer experience.
Better personalization. Businesses are using LI to provide personalized offers and recommendations to customers based on their location.
Real-time decisions. Location Intelligence helps companies and businesses make decisions in real time. Based on accurate location data, decision makers can always get updated and accurate information.
We recommend you: Location Intelligence Software: How to choose the best one?
How are businesses using LI? (Applications location intelligence)
LI has many applications and use cases in business, including site selection, marketing and sales, and supply chain management.
Retail
Retail companies can use LI to optimize store layouts. Also, identify new store locations, and create personalized offers for customers based on their site location.
Insurance and Finance
Insurance companies can use LI to analyze risks and set premiums. At the same time, finance companies can use it to identify potential fraud.
Real Estate Companies & Urban Planning.
Real estate companies can use LI to identify new investment opportunities, understand infrastructural needs and analyze transit behavior.
Industrial Companies
LI plays a crucial role for industrial companies by enabling them to make more informed decisions based on geographic data. Some use cases are site selection, supply chain management, asset tracking, risk management, and customer analysis.
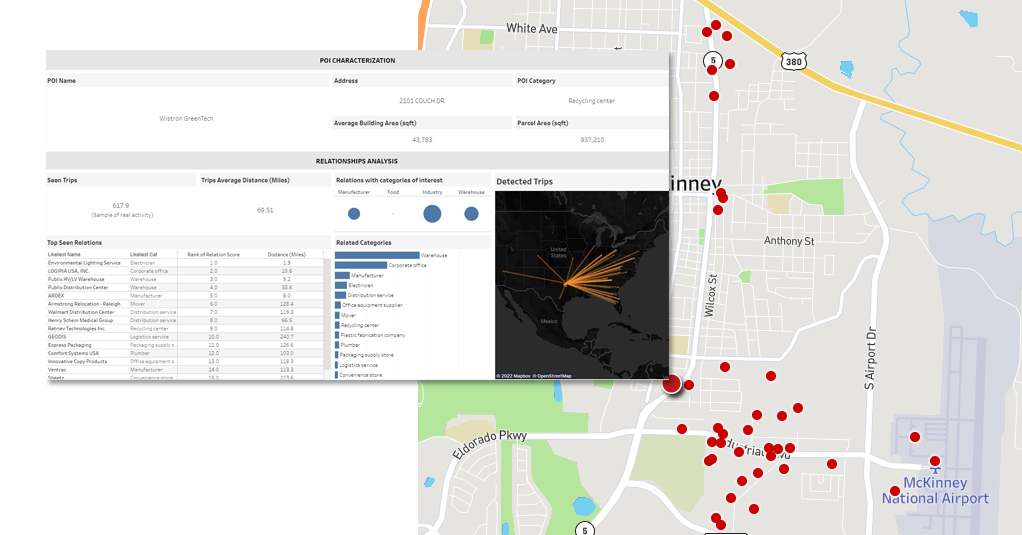
LI for Healthcare
Healthcare institutions are adopting LI for case like:
- Facility planning and management
- Disease and outbreak management
- Telemedicine
- Remote patient monitoring
- Population health management
The role of Location Intelligence in Marketing and Sales
In addition to these specific applications, Location Intelligence softwares can also play a role in marketing and sales. By understanding customers and their behavior, marketers can develop better campaigns and improved sales.
You may also like to read: Location intelligence to optimize commercial strategies
How does Location Intelligence work?
Location Intelligence (LI) collects, analyzes, interprets, and implements location-based data to make business decisions. LI collects and analyzes various data types, such as:
- Demographic information
- Customer behavior
- Historical data
And then displays them on a map. This data is later used to identify patterns and trends.
The role of Location Data in LI
Location data is an essential ingredient for Location Intelligence, as it provides information about the location of customers and objects. When combined with other data and analyzed, it is helpful to make informed decisions, optimize operations and improve the customer experience.
Location data refers to information that includes information about a location or an object’s position on earth. It can be in the form of coordinates, addresses, or other location-related information.
Location Data is collected from various sources such as GPS devices, mobile apps, and social media. This data can also be purchased from third-party providers.
The 6-step process of location data
We must consider that this process is cyclical. Data is constantly updated, analyzed, interpreted, and implemented.
Step 1. Data Collection.
Data can come from various sources such as GPS devices, social media, mobile apps, and third-party data providers. The data collected includes customer location, demographic information, and historical data.
Step 2. Data Cleansing
Once the data is collected, it needs to be cleaned and prepared for analysis. This step involves removing duplicate or irrelevant data (This ensures that data is accurate and has the correct format).
Step 3. Data Analysis
Next step involves analyzing the data to identify patterns and trends. This step uses geographic information systems (GIS) and geospatial analysis techniques to map and visualize the data.
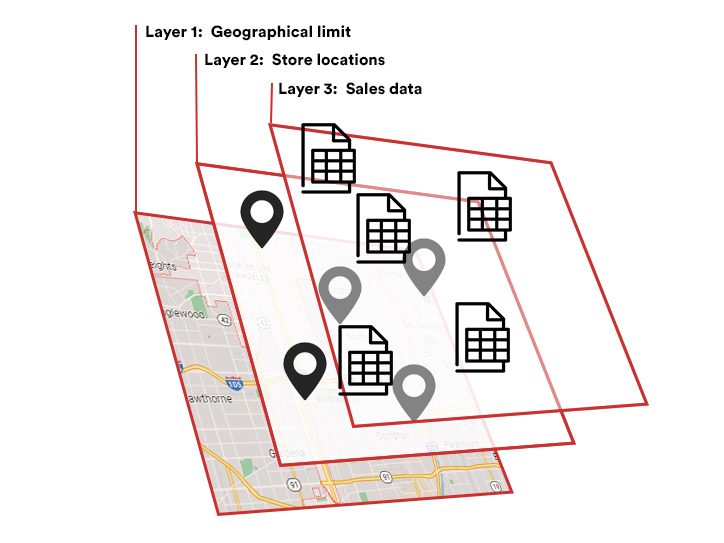
Step 4. Data Interpretation
Data needs a correct interpretation to make meaningful insights. This step involves using business intelligence techniques to turn the data into actionable information.
Step 5. Data Implementation
The final step is to implement the insights gained from the data. For better insights, it needs to be presented in real-time.
Step 6. Data Monitoring
This should always be an additional step. It is crucial to monitor the results and make adjustments as needed. This step involves tracking the success of the changes made and making adjustments as necessary to optimize results.
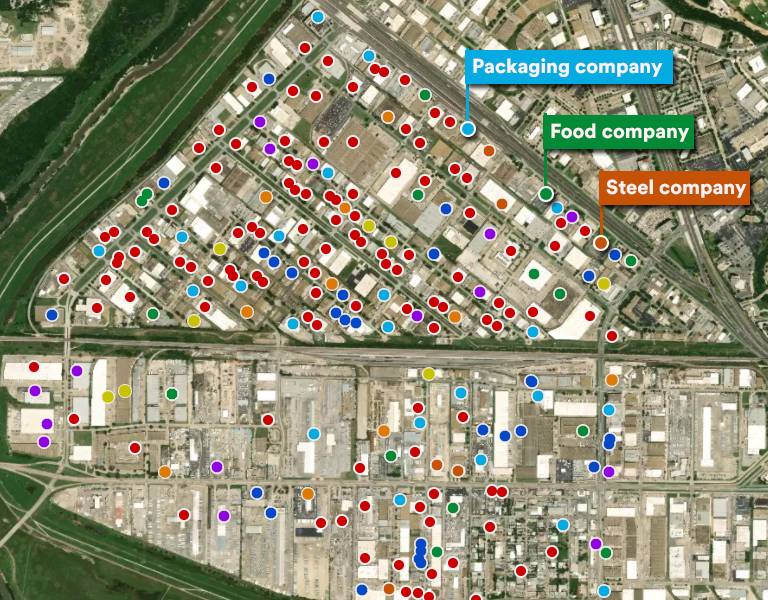
The role of Geospatial Data in LI
Another key component of LI is geospatial data.
Geospatial Data refers to data with a geographic component, such as a store’s location or a neighborhood’s boundaries. This data is crucial for LI as it provides a visual representation (Providing easier understanding and interpretation).
The challenges of Location Intelligence
Although Location Intelligence has excellent benefits for companies, it also comes with challenges. Businesses need to be aware of these challenges and take steps to address them.
Challenge 1: Ensure Data Quality
One of the main challenges of LI is ensuring that the data used is accurate and reliable. Data quality issues can appear due to errors in data collection (Such as incorrect GPS coordinates or missing data).
Challenge 2: Maintain Data Privacy
Another challenge of LI is ensuring that data privacy is protected. Location data can contain sensitive information, so businesses requires to comply with data privacy laws and regulations.
Challenge 3: Keep Data Integration
Integrating location data with other data types, such as demographic information and customer behavior, can be challenging. Data must be in the correct format and easily integrated with other systems.
Challenge 4: Have effective Data Management
Managing and storing large amounts of location data can be challenging. Businesses must ensure the necessary infrastructure and resources to handle the data.
Challenge 5: Develop Data Security Protocols
Location data can be vulnerable to cyber threats and data breaches. That is why businesses must develop correct security measures to protect their data.
Challenge 6: Need for Technical Expertise
LI requires specialized technical expertise, including knowledge of GIS, geospatial analysis, and business intelligence. Finding these technical requirements can be challenging for businesses that need to gain the necessary expertise in-house.
How to develop the correct Location Intelligence Strategy?
PREDIK Data-Driven is a company that specializes in helping businesses develop a Location Intelligence (LI) strategy.
With our team of data experts in geographic information systems (GIS), geospatial data, and business intelligence, we can help businesses to collect, analyze, and interpret location-based data to make data-driven decisions and gain a competitive edge.



