Retail analytics involves leveraging data and analytical techniques to enhance the performance of retail businesses. It consists of gathering, cleaning, and analyzing data from various sources such as sales, inventory, customer, and market data.
In this article we will cover the following topics:
Why Is Retail Analytics So Important?
Retail analytics has eliminated guesswork in many decision-making processes. Consider this: Even the most proficient retail executives must navigate through a vast amount of internal and external data, including factors such as transactional data, merchandise trends, and consumer behavior. Having solid analytics tools simplifies this data and helps retailers make informed decisions in less time and more accurately.
…while retailers are often proud of their acumen, instincts no longer are enough, especially in an industry with narrow profit margins. “
Oracle
As you know, retail is a highly competitive business, made even more complex by the increasing popularity of online shopping. Profit margins in retail have always been slim, leaving little room for error. Minor adjustments in product selection and inventory management can significantly impact stockouts or the need for steep discounts, which can dramatically affect the bottom line. For example, fashion retailers can use data analytics to determine which styles and sizes to order for different locations based on demographic and purchasing trends at each site.
By using retail analytics systems, decision-makers understand purchase behavior based on demographics, store location, seasonality, and available stock, among others.
We recommend you reading: Understanding the role of Big Data in Retail Industry (With Examples)
Six benefits of using Analytics for retail
Better sales intelligence
Retailers can use analytics to identify top customers, optimize pricing, and improve marketing campaigns for increased sales.
Reduced costs
Brands can minimize inventory costs, improve supply chain efficiency, and optimize staffing levels. This optimization can lead to lower overall costs and improved profitability.
Improve customer satisfaction
Retail analytics provide insights into customer needs and preferences, leading to personalized shopping experiences that enhance customer satisfaction and loyalty.
More refined targeting for marketing campaigns
Marketers can improve campaigns by identifying effective ways to reach and engage target customers, resulting in higher ROI.
Enhanced customer experience and loyalty
Data analytics helps retailers improve customer loyalty by addressing pain points and creating seamless shopping experiences.
We recommend you reading: How to Get Useful Customer Behavior Analytics?
Better staff scheduling
Retail analytics tools assist decision-makers in predicting customer demand and scheduling staff, leading to enhanced customer service and reduced labor costs.
In addition to these six main benefits, retail analytics solutions can also:
- Improve product development: Decision-makers can develop new products based on current trends and customer needs.
- Optimize pricing: Analytics models can help retailers set the optimal prices for their products, considering factors such as demand, competition, and cost of goods sold.
- Reduce fraud: Companies can use customer behavior analysis to identify and prevent fraudulent transactions.
- Make better business decisions: Brands can rely on accurate retail data reports to optimize business decisions for inventory, marketing, and store operations.
Types of retail analytics: Four different approaches
In retail, there are four primary types of data analytics: Descriptive, Diagnostic, Predictive, and Prescriptive.
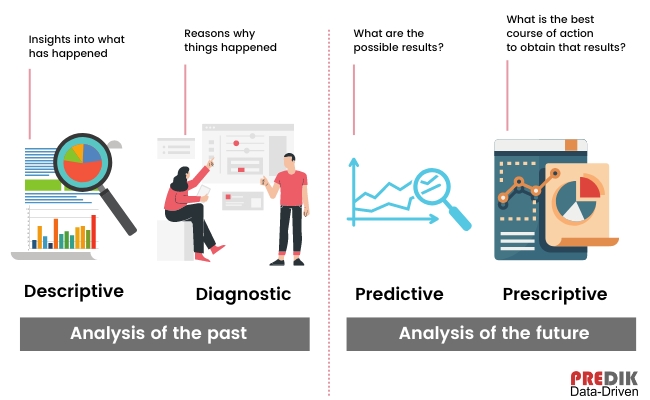
Descriptive approach
This is the fundamental type of data analysis used in retail. It answers what happened in the past, such as the total number of product units sold in the previous week or the average amount customers spent. Through descriptive analytics, you can create reports and dashboards that offer retailers a quick look at their business performance.
Diagnostic approach
Diagnostic analytics goes a step further and tries to answer why something happened. It uses data to identify the underlying causes of problems and opportunities. For instance, a retailer can use diagnostic analytics to find out why sales of a specific product are decreasing or why customers are leaving their shopping carts.
Predictive approach
Predictive insights use data to forecast future events and trends. For retail, it can help make better decisions about pricing, product development, marketing, and more.
We recommend you reading: Predictive Analytics In Retail: How It Works? (5 Big Benefits + Use Case)
Prescriptive approach
This is the most advanced type of retail data analytics. It leverages data to provide specific and actionable recommendations to retailers, enabling them to improve their overall business performance.
For example, prescriptive analytics can suggest which products to stock, identify optimal locations for new stores, or help retailers allocate their marketing resources more effectively.
Different uses of retail data analysis
When planning data collection and analysis for retail analytics, it’s essential to start with the questions you want to answer. This way, you can categorize the data into valuable levels depending on whether you wish to analyze customers, store operations, the whole company, or individual transactions.
It’s important to note that not all categories will apply to every company. For example, if you only sell through physical stores, multichannel analytics will not be helpful.
Shopper-level analytics
Analyzing how customers interact with a brand and its products is the primary objective of shopper-level analytics. It enables businesses to track consumer behavior, such as their movements in a physical store, the web pages they visit on a website, and the products they buy.
The information gathered helps improve the overall customer experience and increase sales.
Transaction-level analytics
Transaction-level analytics tracks individual transactions, including purchase details, payment methods, and timestamps. This data is valuable for improving marketing campaigns, measuring sales success, and detecting fraud.
On-shelf analytics
On-shelf analytics helps keep track of data such as the rate of sale, popularity, and unpopularity of products. This data enhances inventory management and product placement.
Location analytics
Analyzing customer shopping patterns is the primary focus of location analytics. It enables businesses to track valuable data, for example, which stores and products are the most popular in different regions and how customers travel between stores. This data improves store placement, product selection, and marketing strategies.
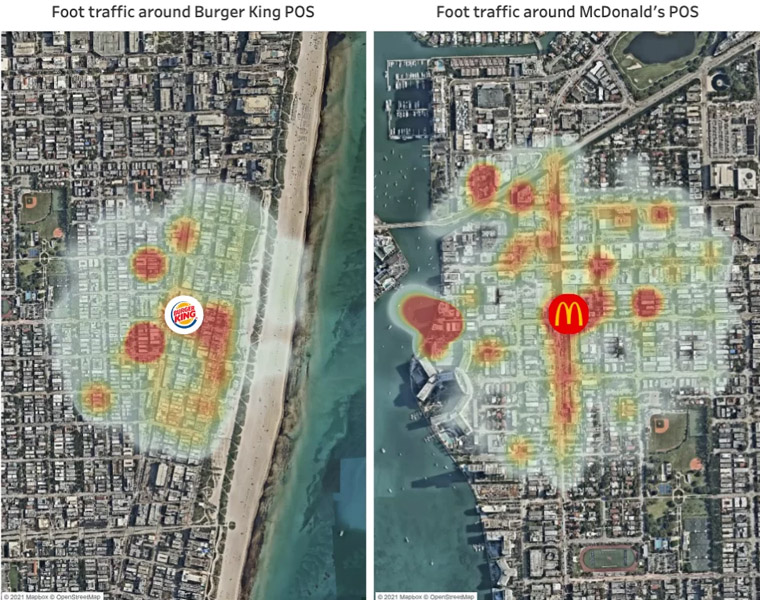
This article can also be helpful for you: How Does Location Intelligence Work & Why Do You Need It?
Multichannel analytics
Multichannel analytics focuses on customer interactions with a brand across multiple channels. It helps to track and analyze data such as customer channel preferences, product purchases, and how they navigate between channels. This information improves the overall customer experience across all channels.
Outcome-level analytics
This type of analytics tracks retail operations’ results, such as sales, profits, and customer satisfaction, identifying trends and areas for improvement.
Use case: How Walmart uses retail analytics
Walmart uses retail analytics to enhance its operational efficiencies, gain insights into customer behavior, optimize its supply chain management, and ensure a secure environment for data analysis. As a result, they have not only improved their customer experience but also gained a competitive advantage in the retail market.

Some examples are:
Operational Efficiency: Through retail analytics, Walmart processes multiple terabytes of data daily. This process has led them to a 10% to 15% increase in online sales, amounting to $1 billion in added revenue.
Understanding Customer Behavior: By harnessing the power of social media and mobile big data analytics, Walmart grasps customer preferences and behaviors. For instance, by evaluating social media data, they identify market trends, react promptly to customer requirements, and even use mobile analytics to personalize customer recommendations.
Understanding Customer Behavior: By leveraging the potential of social media and mobile analytics, Walmart gains insights into customer preferences and behaviors. For example, by analyzing social media data, they can identify market trends, respond quickly to customer demands, and even use location analytics to provide personalized customer recommendations.
Optimized Supply Chain Management: Some Walmart stores have implemented shopping carts equipped with sensors that collect data on inventory, product placement, and consumer behavior. This data is used to optimize supply chain operations and improve product availability.
Our tips (Best practices) if you want to use retail analytics for your strategies
Be clear on your goals. What do you want to achieve with retail analytics? Do you want to increase sales, improve customer satisfaction, or reduce costs? Once you know your goals, you can collect the necessary data.
Collect the correct data. Not all data is created equal. When collecting data for retail analytics, it’s essential to ensure it is accurate, relevant, and complete. For example, usually, data sources for retail analytics include point-of-sale systems, e-commerce platforms, loyalty programs, and customer surveys.
Learn how to integrate your data. Once you have collected your data, you must incorporate it in a way that makes it easier to analyze your data and get insights.
Use data visualization tools that will help you identify key insights. Data visualization tools make it easier to understand and communicate data, so you must choose wisely.
Analyze your data regularly. Retail analytics is not a “one-time” event. You need to analyze your data regularly to identify trends and patterns. This will help you to make better business decisions over time.
What to expect from Retail Analytics in the following years?
Oracle estimates that soon, retail analytics will be more prevalent yet less noticeable and discussed. Users and applications will utilize analytics more frequently, often without even realizing it. This will differ from the way smartphones regularly employ location tracking to address users’ requirements promptly.




